International Baccalaureate Diploma Programme
Here at The Koç School we offer students the opportunity to experience a truly international education.
The International Baccalaureate Diploma Programme (IBDP) is open to students from Grade 11 onwards, forming a challenging but balanced two year programme of study in a range of subjects. The design of the course, assessments and final examinations prepare students for success at university and in their future beyond education. The programme is highly respected by the world’s leading universities and is currently on offer in 3,104 schools in 147 different countries around the world.
The IBDP aims to provide an education which balances subject breadth and depth, as well as encouraging broader disciplines through its core components: the unique Theory of Knowledge course, the Extended Essay and CAS (Creativity, Activity, Service). The course aims to promote international-mindedness, including the study of mother tongue language and culture, within the goal of preparing IB students for university education and beyond.
The whole person is developed through rigorous external and internal assessments, as well as the physical, intellectual, emotional and ethical aspects of the programme.
Please see individual subject pages for further information on IB subjects.
To meet the requirements of the programme, students choose six courses to study at Higher and Standard Level from a range of options, including languages, social and natural sciences, mathematics and the arts. Throughout these courses students will gain a deep understanding of the IB Learner Profile. The ten aspirational qualities of great learners are listed as inquirers, thinkers, communicators, risk-takers, knowledgeable, principled, open-minded, caring, balanced and reflective. These are the qualities that Koç IB students are inspired and motivated by.
In addition to the classroom study, students widen their education with a core element which challenges their understanding, knowledge and experience. The core consists of:
- Extended Essay, which enhances research skills and independent learning.
- Theory of Knowledge, which encourages students to reflect and critically examine through language, reason, emotion and perception.
- Creativity, Activity, Service, which offers students the opportunity to involve themselves in real tasks beyond the classroom.
What is CAS?
CAS consists of three strands: Creativity, Activity and Service.
Creativity aims to improve the creative thinking capability mostly observed in different forms of art.
Activity aims to develop the physical capacity of the student, usually exemplified in sports.
Service aims to involve students in a social service voluntarily in coordination with or with the help of NGOs.
CAS consists of following actors:
Students: Please see the school guide page 10 for responsibilities of students.
CAS Supervisor: Guides and assists a student to do a CAS activity
CAS Advisor: Guides the students in choosing their possible CAS activity and projects. Monitors them regarding their reflection and CAS experience in ManageBac. For our school, advisors are chosen on a voluntary basis amongst teachers
CAS Coordinator: Responsible for the management of the CAS section of the IB Program
What is ManageBac?
In CAS, the IB office aims to go paperless. To do this we are using a software named ManageBac. All the actors of CAS will monitor the CAS activities in ManageBac. All the reflection and documentation of CAS will be uploaded to ManageBac.
How is CAS activity formed on ManageBac?
Stage 1: The student has an interview with his/her CAS advisor. Decides on the possible activities and finds his/her CAS supervisor
Stage 2: The student adds his/her activity on ManageBac by completing forms and submitting the learning outcomes, the supervisor and planned CAS experiences.
Stage 3: The CAS Advisor of the student approves the activity
Stage 4: When the activity is completed, it is approved once again by the CAS advisor and the planned CAS experience is realized.
Is there a CAS Hour limit?
We are not counting hours in CAS anymore. However, achieving 7 learning outcomes and finding the balance between three strands (Creativity, Activity, Service) is the main part.
What is TOK?
TOK explores questions about knowledge and the process of knowing. In more depth; TOK emphasizes comparisons and connections between areas of knowledge and encourages students to become more aware of their own perspectives and the perspectives of others.
TOK focuses on answering the question “How do we know?” something, helps you to critically analyze the ways in which you gain knowledge in broad subject areas and provides you with an opportunity to explore and reflect on the nature of knowledge and the process of knowing.
In TOK, students reflect on the knowledge, beliefs and opinions that they have built up from their years of academic studies and their lives outside the classroom. The course is intended to be challenging and thought-provoking—as well as empowering—for students.
The TOK course plays a special role in the DP by providing an opportunity for students to reflect on the nature, scope and limitations of knowledge and the process of knowing. In this way, the main focus of TOK is not on students acquiring new knowledge but on helping students to reflect on, and put into perspective, what they already know.
TOK underpins and helps to unite the subjects that students encounter in the rest of their DP studies. It engages students in explicit reflection on how knowledge is arrived at in different disciplines and areas of knowledge, on what these areas have in common and the differences between them. It is intended that through this holistic approach, discussions in one area will help to enrich and deepen discussions in other areas.
The course is an opportunity for teachers and students to engage in interesting conversations that cross the boundaries of individual disciplines and that help students to reflect on the knowledge they have acquired from both their academic studies and their lives outside the classroom
In TOK, we are not necessarily interested in the content of knowledge claims; instead, the main focus is on asking the question: How do you know? In the current political and social discourse and on social media, people often obsess about what others think rather than spending time to examine the hows and whys behind their beliefs and claims to know. This is where TOK is necessary for students in the DP.
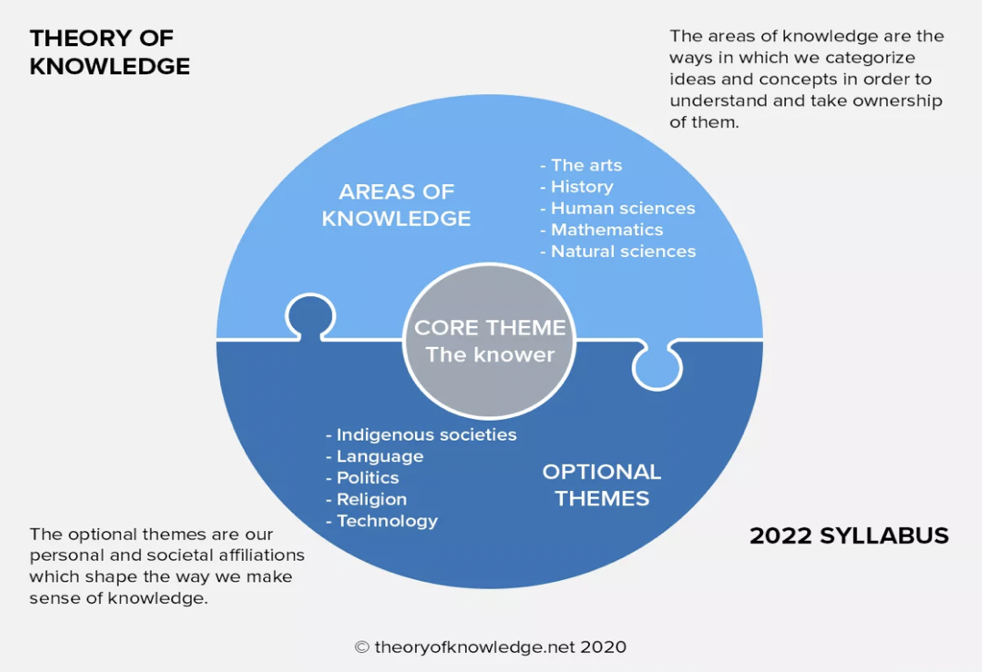
Within TOK classes, we explore the BQs within the context of five different ‘areas of knowledge’ (AOKs) and five optional themes. These elements of TOK are best visualized via this diagram. It places the core theme The knower in the Centre, surrounded by the Optional themes (personal and societal affiliations we shape the way we make sense of knowledge) and the AOKs on the top blue ring (the categories that we place the knowledge in).
The aims of the TOK course are:
- to encourage students to reflect on the central question, “How do we know that?”, and to recognize the value of asking that question
- to expose students to ambiguity, uncertainty and questions with multiple plausible answers
- to equip students to effectively navigate and make sense of the world, and help prepare them to encounter novel and complex situations
- to encourage students to be more aware of their own perspectives and to reflect critically on their own beliefs and assumptions
- to engage students with multiple perspectives, foster open-mindedness and develop intercultural understanding
- to encourage students to make connections between academic disciplines by exploring underlying concepts and by identifying similarities and differences in the methods of inquiry used in different areas of knowledge
- to prompt students to consider the importance of values, responsibilities and ethical concerns relating to the production, acquisition, application and communication of knowledge.
Assessment of TOK:
TOK has two assessments; one internal and one external.
The Internal Assessment is the TOK Exhibition where students create an Exhibition based on either the core theme or one of the optional themes. Students choose three objects of significance to their lives and link it through one of the 35 IA prompts published by the IBO. This is marked by the teacher of the class and overall is 1/3 of the TOK grade of the student.
The External Assessment is the TOK Essay where students choose one of the 6 prescribed titles published by the IBO and write an essay with max 1600 words that focus on at least one of the Areas of Knowledge. This is marked by the IB examiners and overall is 2/3 of the TOK grade of the student.
What is the Extended Essay?
The extended essay forms part of the IB Core and like CAS and TOK, is a compulsory part of the IB Diploma Programme.
It is externally assessed piece of independent research into a topic chosen by the student and presented as a formal piece of academic writing. It is intended to promote high-level research and writing skills, intellectual discovery and creativity while engaging students in personal research. The end product is a major piece of formally presented, structured writing of up to 4,000 words in which ideas and findings are communicated in a reasoned, coherent and appropriate manner.
The Extended Essay is designed to provide students the opportunity to:
- Use intellectual initiative and rigour to engage in independent research
- Develop research, thinking, self-management and communication skills
- Reflect on what has been learned throughout the research and writing process.
Students are supported through the Extended Essay process by an EE supervisor. Throughout the process, students are required to have three mandatory meeting and reflection sessions with their supervisor.
How is the Extended Essay assessed?
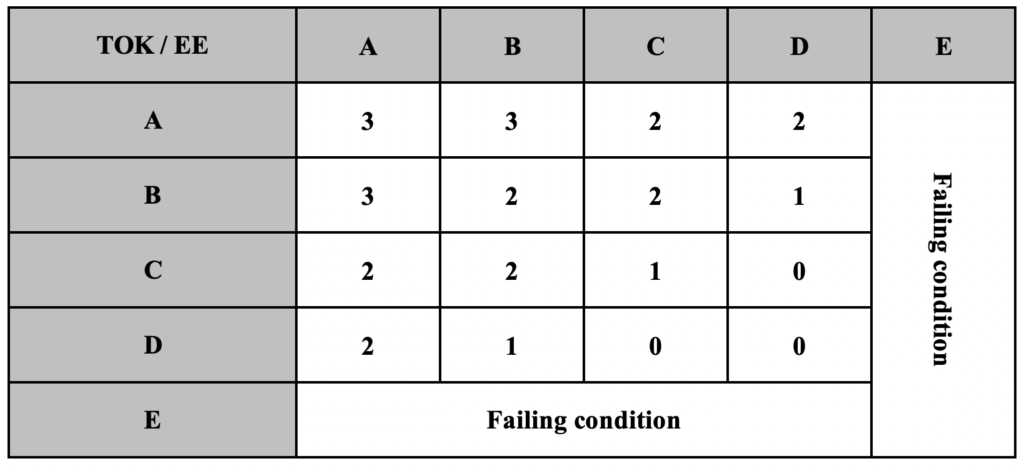
The essay is marked by an external examiner and will be awarded a grade on the scale A to E. This grade is then combined with the grade for TOK to create a mark out of 3 points towards the whole diploma score.
The TOK/EE matrix is shown below: